Our insights on the industry’s most pressing challenges



Compliance challenges on the Paris Air Show
Tous les deux ans, le Salon international de l’aéronautique et de l’espace du Bourget s’impose comme un rendez-vous majeur pour les entreprises de la base industrielle et technologique de défense (BITD). Vitrine mondiale du savoir-faire français et européen, le Bourget est aussi, pour les industriels de la défense, un espace d’exposition sensible, soumis à des risques de conformité particuliers que trop peu d’acteurs anticipent réellement.


NATO's critical raw materials list: legal and strategic stakes for the defence industry
The escalating rivalry between China and the United States has placed rare minerals at the center of geopolitical tensions, challenging supply chain stability for industries worldwide. This article explores why these critical materials are indispensable to advanced defense technologies and how French defense companies can mitigate risks associated with China’s market dominance through strategic innovation and collaboration.


The legal review of weapons: what defense companies need to know
International humanitarian law requires states to ensure that the use of "a new weapon, means or method of warfare" is authorised. To comply with this obligation, when new weapons are studied with a view to equipping their armed forces, they must undergo a legality review. Companies designing equipment for the armed forces must include this review at the research and development stage.

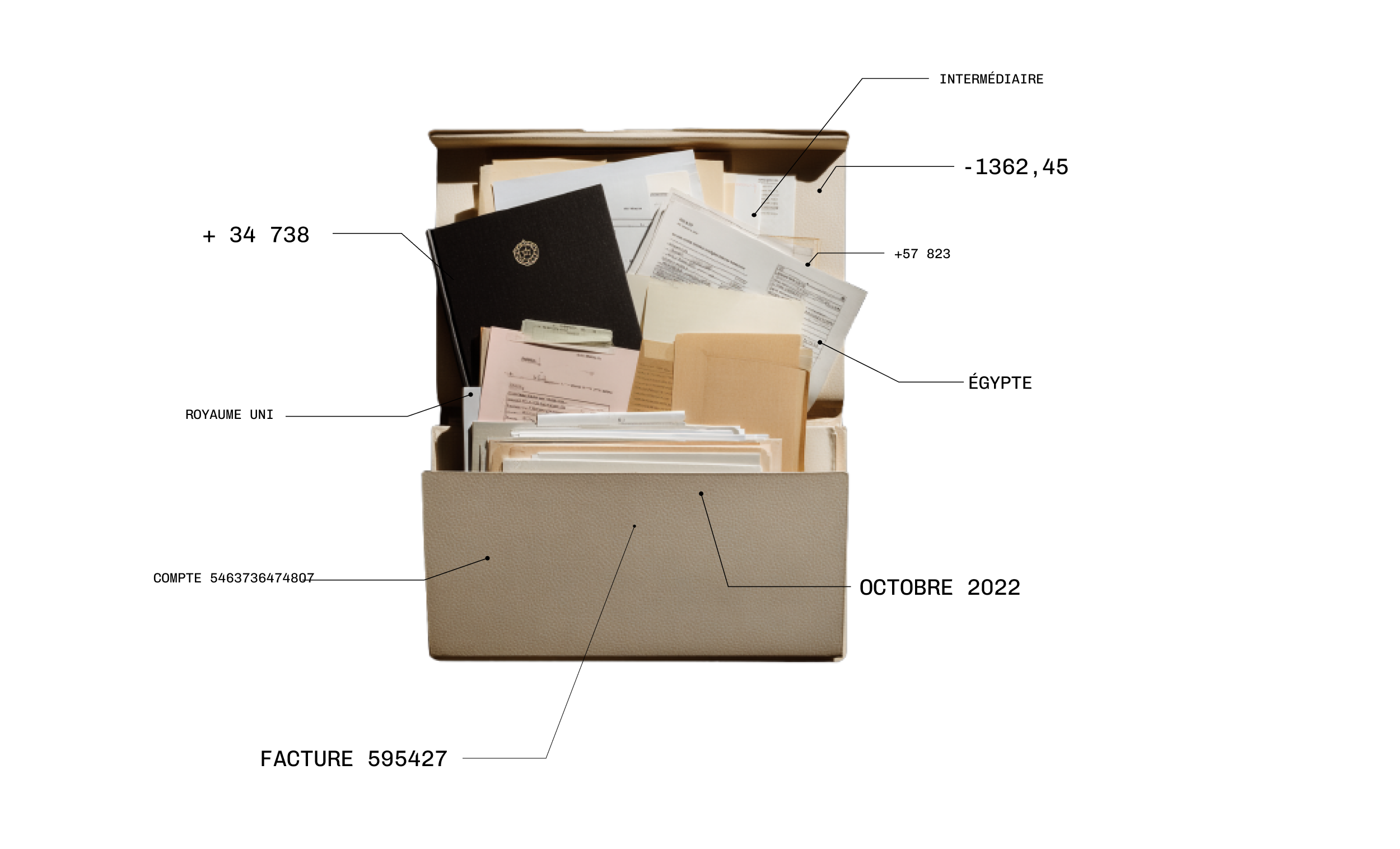
Defence SMEs: 9 considerations to initiate a compliance programme
Companies that design military equipment and dual-use goods and technologies shoulder significant responsibilities. To prevent the risk of corruption, that of using goods and technologies to commit serious violations, or of harming national interests, vigilance is required on many fronts. While major groups have dedicated teams and are often in the vanguard when it comes to compliance, the defence industry also consists of many SMEs and start-ups, for whom the subject may seem daunting. The aim of this guide is to help them with their initial thoughts on the subject.

Military equipment trade: export licences in criminal defence
As the movement to hold corporations to account for their participation in human rights violations grows, one sector in particular is at risk: the defence industry. Under the impulse of human rights organisations, several investigations and prosecutions are already ongoing to identify the role played by corporations and their executives in the war crimes and crimes against humanity allegedly perpetrated with equipment they sold to state and non-state actors. A number of factors explain the lack of readiness amongst legal departments facing such challenges. The main one seems, however, to reside in the overconfidence provided by the export licences delivered by their state. Corporations assume, mistakenly, that the licence to export awarded by the state shields them and their executives from criminal accountability.

Legal challenges for the defence industry: a long term vision
A legal risk is arising for the defence industry: that of prosecutions against the company and its executives on the charges of complicity for international crimes. While the accountability of corporations for their role in war crimes and crimes against humanity was already addressed during the Second World War, with, for instance, the prosecution of Krupp during the Nuremberg Trial, it had somewhat been relinquished, becoming a substantial matter again only over the past twenty years. Increasingly, indeed, scholars have reflected on the responsibility arms manufacturers bear in the perpetration of war crimes, crimes against humanity and genocide, when these violations are perpetrated with the weapons they have sold to the alleged perpetrators. So have practitioners.

Accountability for civilians participating in cyber operations
Increasingly, states partner with non-state actors to ensure the defense of their interests in the cyber space. Understanding the status of those actors, who may be called to perform cyber operations against foreign state actors, proves arduous. Such entities play a significant role in the defense of the interests of the states, and in the case a conflict arises, they might be included in the defense of the interest of the state. In case of an international armed conflict, some of the companies participating in this type of coordination initiative and their employees may therefore participate in operations contributing to an armed conflict.

